Healing Journey Insights & Tools
- Home
- Blog
- Mitochondria
- Mitochondrial Toxicity & Stunting Our Energy Production: An Epidemic of Mass Proportions?
Mitochondrial Toxicity & Stunting Our Energy Production: An Epidemic of Mass Proportions?
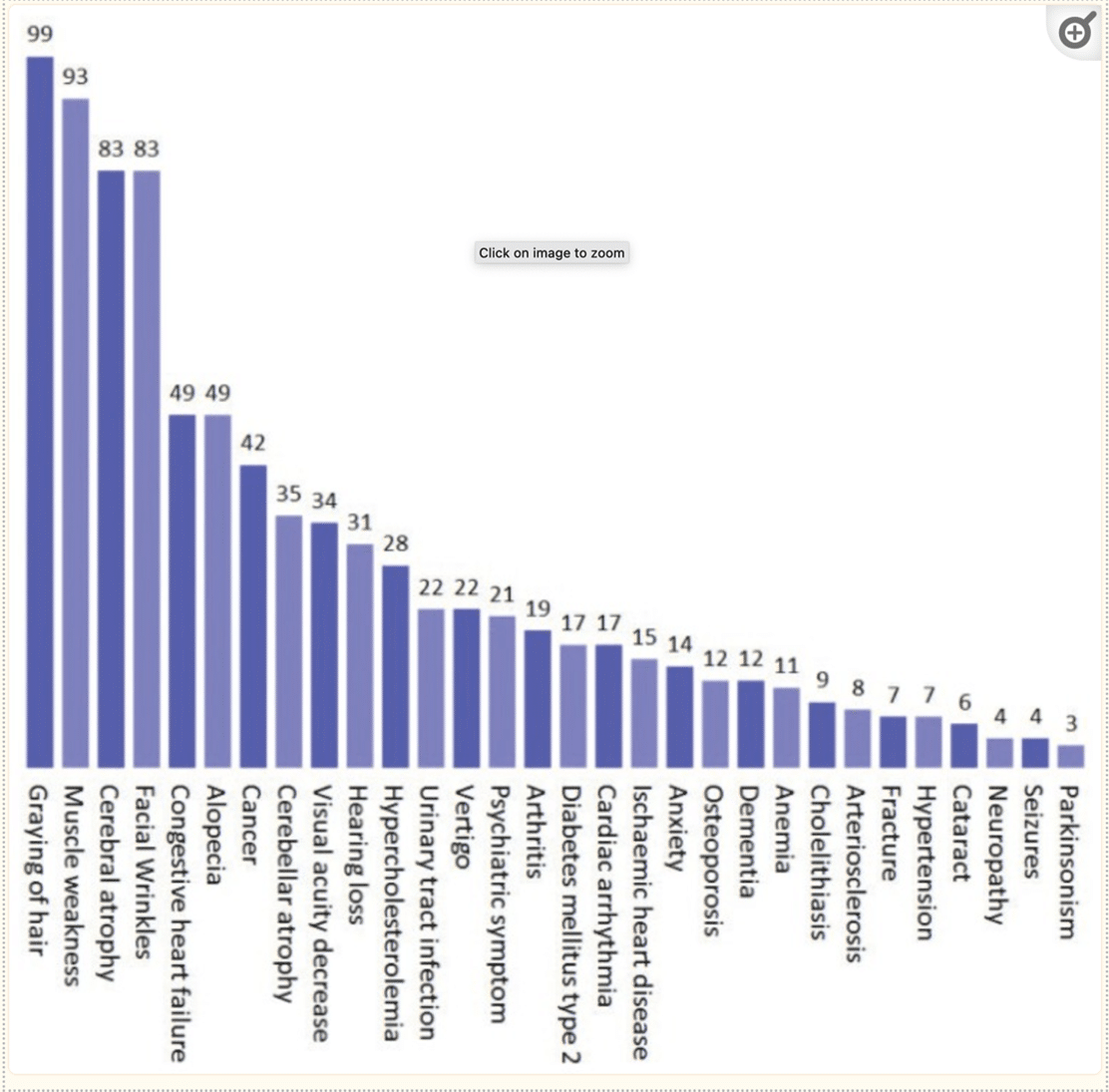
Ok, that may sound important, but how do I make this digestible on a practical scale? The graph below shows the probability that a certain condition has its roots in mitochondrial dysfunction. There are quite a few here and likely many more we don’t fully understand yet. The point is that mitochondria may not seem that important, but they are. They not only make energy, but play a role in cellular communication, signaling, immunity, and apoptosis (turning off and killing rogue cells or dying cells-often known as autophagy, but in the mitochondria, it is known as mitophagy). The good news is that there are practical ways to support mitochondria, improve function and increase longevity.
“A large amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) must be produced by the mitochondria every second of every day because ATP cannot be stored. This function is so important that mitochondria can take up as much as 25% of the cell volume. Cells contain from 1000 to 2500 mitochondria. The average cell uses 10 billion ATP per day, which translates to the typical adult needing 3.0 × 1025 ATP (I am publishing these numbers with some trepidation as the research is surprisingly inconsistent about exactly how much ATP a cell needs). To accomplish this prodigious feat, each ATP needs to be recycled from ADP 1000 times per day. Because the body cannot store ATP, the mitochondria must function consistently all the time. At any given time there are about 250 g of ATP in the cells. This represents about 4.25 watts, the equivalent of the energy in an AA battery. Every day, a healthy person produces a remarkable 1200 watts. Because the brain uses 70% of ATP, this helps explain the strong correlation between mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration.” Dr. Joe Pizzorno, ND quoted in the Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal
So right off the bat, we can see that mitochondria play a role in constantly making energy for us and the cells that contain the most mitochondria are in the brain! The heart, liver, kidneys, and ovaries are at close seconds. Many drugs have been taken off the market due to their mitochondrial toxicity, which caused a plethora of disease symptoms in patients.
You may be wondering, what are my top ten toxins, metals, pathogens, or medications that damage mitochondria? So here they are, in no order:
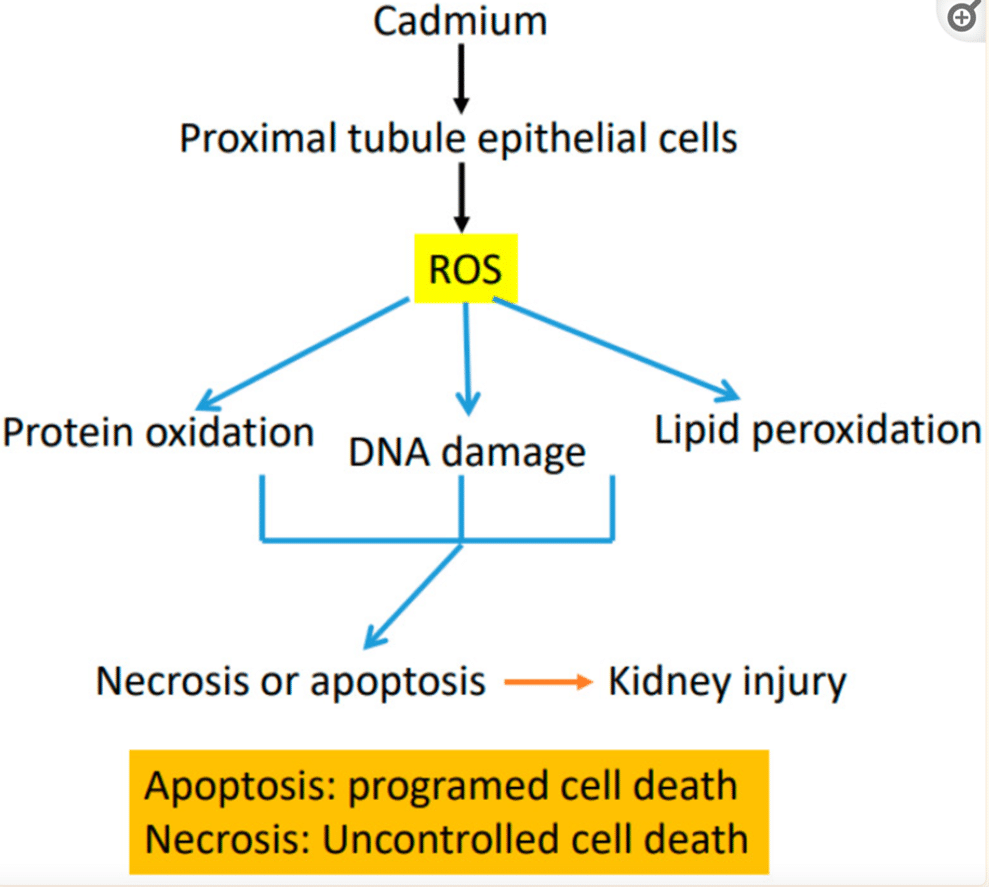
- Cadmium (kidney mitochondria)-Cadmium is a heavy metal found commonly in vapes (for you kiddos) and can also be found around air pollution, cigarette smoke, and in certain grains and rice. Studies have demonstrated that upon exposure to cadmium, kidney mitochondria displayed deformation, swelling, and vacation, concurrent with increased reactive oxygen species which can damage DNA. This can cause chronic kidney disease. Want to learn to properly do a heavy metal detox? Find my Heavy Metal protocol HERE (Promo code: DRJESSBLOG)
- Pesticides-Certain pesticides, namely organophosphates and carbamates, cause direct damage to the mitochondria through the Krebs cycle. As we mentioned above, the brain has the most mitochondria, so damage to them would affect neurocognition first. We now suspect pesticides are the root cause of Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative conditions and they do so by attacking mitochondrial complexes as well as augmenting the documented effects of disruption of acetylcholine signaling (useful for movement).
- Mold and Lyme disease, also known as biotoxin illness-most studies nowadays are showing how mycotoxins, metabolites that are made by mold species, can damage our DNA by producing volatile organic compounds. In one study, the researchers reviewed 6 case studies and participants received blood tests for autoimmune, metabolic, hormonal, and nutritional parameters, including AMA. Six participants with documented mold and water damage also had elevated AMA (anti-mitochondrial antibodies). Want to learn how to do a proper mold detox? Find my MOLD protocol HERE (Promo code: DRJESSBLOG)
- Covid miRNA vaccines and Covid– Many people infected with the SARS-CoV-2 suffer long-term symptoms, such as “brain fog”, fatigue, histamine issues, and clotting problems. Remember if the virus can cause these symptoms, the vaccine can reproduce those symptoms in sensitive individuals. In some studies, in individuals with prior sub-optimal mitochondrial function, the virus can “tip” the host into a chronic inflammatory cycle. This might explain the main symptoms, including platelet or clotting dysfunction. Long COVID, from the virus or the vaccine, could thus be described as a chronic and self-perpetuating metabolically imbalanced non-resolving state characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, where reactive oxygen species continually drive inflammation and a shift towards glycolysis (this means there’s not enough energy to get into the Kreb’s cycle and make all the ATP needed). Find My COVID Long haulers protocol HERE – get rid of your long COVID for GOOD! (Promo code: DRJESSBLOG)
- Genomic instability or genetic predispositions (whether inherited from your parents or the environment’s negative effects)-looking at data, we know now that the APOE4 gene predisposes someone to mitochondrial fragility. Studies demonstrate that APOE4 expression is associated with altered mitochondrial dynamics, which might lead to impaired mitochondrial function in astrocytes, a specialized type of brain cell. This, in turn, may contribute to the pathological effects of APOE4 in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Alcohol and cocaine- The metabolism of alcohol and cocaine are closely linked with the stimulation of reactive oxygen species generation and oxidative stress which damage DNA. Point blank alcohol and cocaine age you.
- Persistent organic Pollutants (POP) and forever chemicals –are chemicals that resist biodegradation in the environment and negatively impact human health. Examples include DDT, dioxins, PFAS and flame retardants, PCBs, and many pesticides. They are lipophilic and accumulate in fat tissue. POPs are linked to the development of diabetes, a mitochondrial-dependent condition. In fact, in one study, These results demonstrate that the study reflects real environmental conditions, with low-dose and multiple-toxin exposure for a long period, that POPs alter major mitochondrial enzymes’ functions with an imbalance of redox homeostasis in a sex-dependent manner (males affected more with oxidative markers and females affected more with mitochondrial activity markers). Want to test to see your environmental toxin load? Order your OWN tests at a HUGE discount, HERE!
- Mercury- Mercury, the toxic heavy metal found in amalgams, vaccines, and fish, can disrupt the mitochondrial electron transport chain, induce glutathione (the major antioxidant) depletion, oxidative stress and increase reactive oxygen species levels, damage the mitochondrial membrane, and induce mitochondrial swelling and cell death signaling. Also, this heavy metal has a high affinity for binding to sulfhydryl groups in mitochondria. This is how mercury is associated with so many different symptoms and diseases; it is linked to mitochondria damage in so many organs. Find my Heavy Metal protocol HERE!
- Prescription drugs- Two drugs that still impede mitochondria are statins like Rosuvastatin and antibiotics, specifically the fluoroquinolones like ciprofloxacin. Statins, the famous cholesterol drugs, damage mitochondria by depleting CoQ10, used as a cofactor in the mitochondria. Some antibiotics not only impair ATP production; they also increase reactive oxygen species production (make you age) and damage mitochondrial DNA. No bueno since mitochondrial DNA does NOT have the same repair mechanisms as regular DNA. The degree of mitochondrial DNA damage can be indirectly measured by 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in the urine. (YOU CAN GET THIS ON THE DUTCH TEST HERE) Drugs including Tylenol, aspirin, cocaine, indomethacin, and L-DOPA, have been linked to mito damage. Many others have been removed from the market for long-term mitochondrial toxicity that damaged a certain organ, leading to a disease label.
- Trauma- Mitochondrial dysfunction and suboptimal mitochondrial function have been increasingly implicated in several psychopathologies, and recent genetic studies have similarly suggested a pathogenic role of mitochondria in PTSD. Mitochondria play a central role in several physiologic processes underlying PTSD symptomatology, including abnormal fear learning, brain network activation, synaptic plasticity, steroidogenesis, and inflammation. We think the brain may behave and react differently if deficient in organelles that help them produce energy to think and process clearly.
Notable best mention is: aging- Recently, considerable progress in understanding basic mitochondrial genetics and in identifying acquired mitochondrial DNA mutations in aging has been made. Furthermore, the creation of mitochondrial DNA-mutator mice has provided the first direct evidence that accelerating the mitochondrial DNA mutation rate can result in premature aging, consistent with the view that loss of mitochondrial function is a major causal factor in aging. Yes, mitochondrial damage is inevitable and unavoidable.
Some necessary cofactors and vitamins used in ATP production (that you should use in your protocols) include:
- B vitamins
- CoQ10
- FAD
- NADH
- Cysteine
- Magnesium
- Carnitine
Here are Dr. Jess’s favorite ATP-boosting supplements:
- BC ATP (Code: sIUn3TNM)
- Resveratrol
- Alpha lipoic acid
- Quinton minerals
- CoQ10
- NAD+
- Acetyl L carnitine (for muscle weakness)
- D ribose
- MitoQ
- The One by Quicksilver Scientific
- B vitamins
- Methylene Blue
Here are Dr. Jess’s Favorite ATP-boosting activities:
- Getting in the sunshine
- Redlight
- Infrared Sauna
- Grounding
- Cold plunges/cold showers
You can heal by becoming your own best doctor.
REFERENCES
Pizzorno J. Mitochondria-Fundamental to Life and Health. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2014 Apr;13(2):8-15. PMID: 26770084; PMCID: PMC4684129.
Yan LJ, Allen DC. Cadmium-Induced Kidney Injury: Oxidative Damage as a Unifying Mechanism. Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 23;11(11):1575. doi: 10.3390/biom11111575. PMID: 34827573; PMCID: PMC8615899.
Leung MCK, Meyer JN. Mitochondria as a target of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides: Revisiting common mechanisms of action with new approach methodologies. Reprod Toxicol. 2019 Oct;89:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 14. PMID: 31315019; PMCID: PMC6766410.
Lieberman A, Curtis L. Mold Exposure and Mitochondrial Antibodies. Altern Ther Health Med. 2020 Nov;26(6):44-47. PMID: 32088666.
Nunn AVW, Guy GW, Brysch W, Bell JD. Understanding Long COVID; Mitochondrial Health and Adaptation-Old Pathways, New Problems. Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 2;10(12):3113. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123113. PMID: 36551869; PMCID: PMC9775339.
Schmukler E, Solomon S, Simonovitch S, Goldshmit Y, Wolfson E, Michaelson DM, Pinkas-Kramarski R. Altered mitochondrial dynamics and function in APOE4-expressing astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 24;11(7):578. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02776-4. PMID: 32709881; PMCID: PMC7382473.
Manzo-Avalos S, Saavedra-Molina A. Cellular and mitochondrial effects of alcohol consumption. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2010 Dec;7(12):4281-304. doi: 10.3390/ijerph7124281. Epub 2010 Dec 21. PMID: 21318009; PMCID: PMC3037055.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323379141_Persistent_Organic_Pollutants_Mitochondrial_Dysfunction_and_Metabolic_Syndrom
Real Progress From
Real People
FREE CARE Plan eBOOK by Dr. Jess, MD.
This system mirrors Dr. Jess MD's steps with patients in her virtual clinic. It’s not a diagnosis, it’s a roadmap; a step-by-step process designed to help people restore function, remove roadblocks, and rebuild resilience.

